Real-Time Streaming with Azure Databricks and Event Hubs
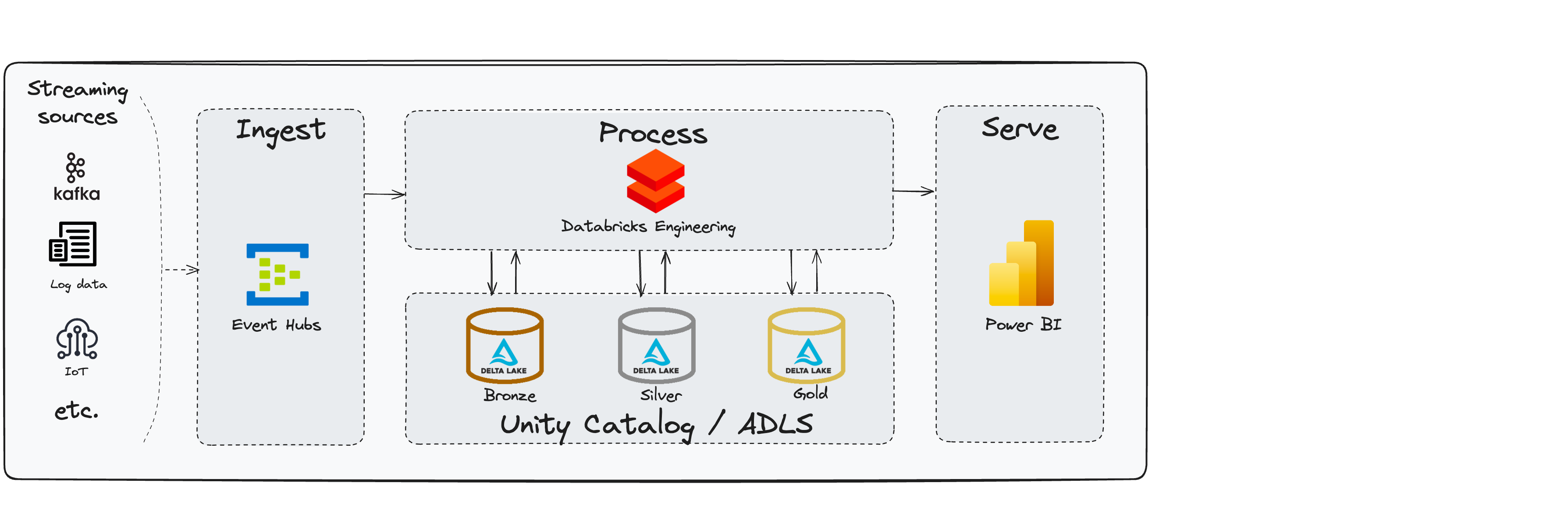
Project Overview
This project demonstrates an end-to-end real-time data streaming solution using Azure Event Hubs, Databricks (with Spark Structured Streaming), Delta Lake, and Power BI for visualization. The project follows the Medallion architecture to process data through Bronze, Silver, and Gold layers.
Architecture Stages
- Ingest: Streaming data from various sources such as Kafka, IoT devices, and log data is ingested into Azure Event Hubs.
- Process: The data is processed using Databricks with Spark Structured Streaming. The data is stored in Delta Lake across Bronze, Silver, and Gold layers.
- Serve: The processed data in the Gold layer is made available for reporting in Power BI.
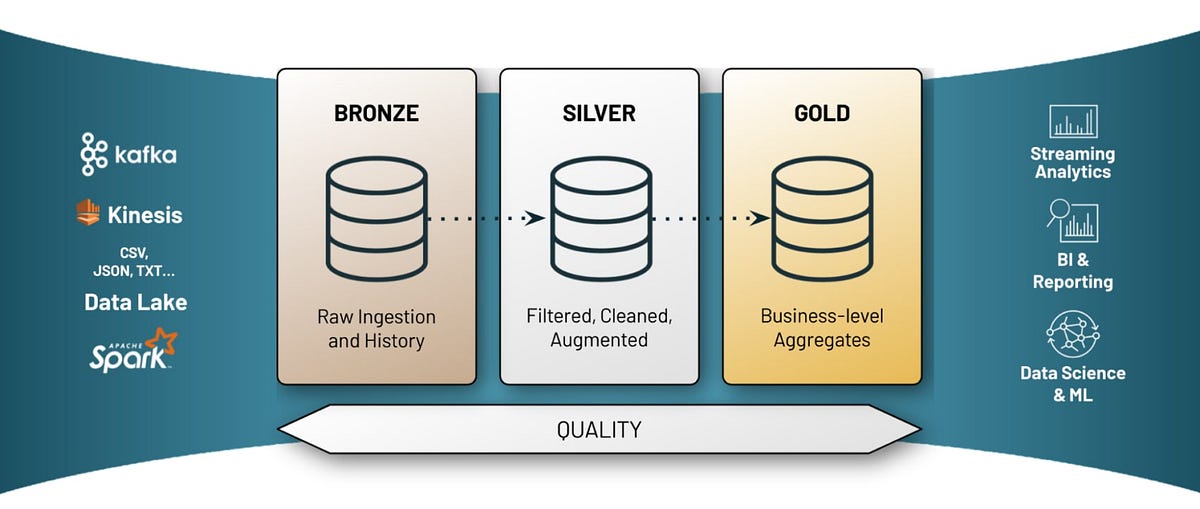
Medallion Architecture
- Bronze Layer: Stores raw, unprocessed data. Minimal transformations are applied to preserve the original data.
- Silver Layer: Data is cleaned, filtered, and enriched. The data is in a more consumable format, ready for business use.
- Gold Layer: Aggregated and refined data is stored. This layer is used for reporting and business intelligence in Power BI.
Medallion Architecture Overview
Azure Event Hubs
Overview
Azure Event Hubs is a big data streaming platform and event ingestion service capable of receiving and processing millions of events per second. Event Hubs can process and store events, data, or telemetry produced by distributed software and devices. It can capture streaming data into an Azure Blob storage or Azure Data Lake for long-term retention or micro-batch processing.
Azure Event Hubs
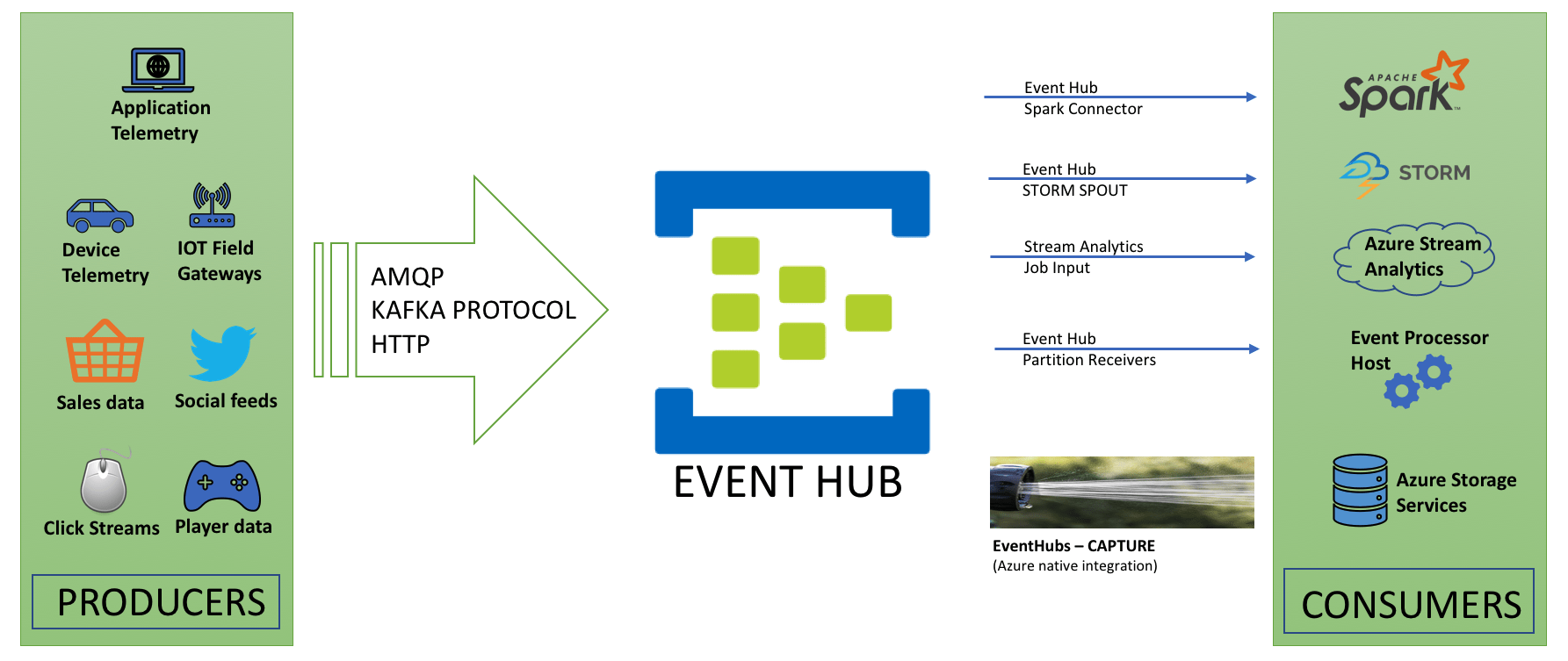
Features
- Real-time Data Ingestion: Event Hubs allows for the ingestion of data in real time with high throughput.
- Partitioned Consumer Model: This model enables parallel processing of data, improving scalability and performance.
- Event Retention: You can configure the retention period for events to ensure that the data is available for the required duration.
- Capture: Automatically capture streaming data into Azure Blob storage or Azure Data Lake Store.
Test Data Generation
In this project, we're generating fake weather data in JSON format. The data includes attributes such as temperature, humidity, wind speed, wind direction, and precipitation. Below is an example of the JSON format used:
{
"temperature": 20,
"humidity": 60,
"windSpeed": 10,
"windDirection": "NW",
"precipitation": 0,
"conditions": "Partly Cloudy"
}
Tools Used
- Azure Event Hubs: For ingesting streaming data.
- Databricks: For processing the data using Spark Structured Streaming.
- Delta Lake: For storing data in a structured format across Bronze, Silver, and Gold layers.
- Azure Data Lake Storage (ADLS): For long-term storage of data.
- Unity Catalog: For managing metadata and ensuring data governance.
- Power BI: For creating reports and visualizing the processed data.
Project Plan
- Data Ingestion: Set up Azure Event Hubs to receive streaming data. Create a Databricks workspace and connect it to Azure Event Hubs.
- Data Processing: Implement Spark Structured Streaming in Databricks to process the data. Store the raw data in the Bronze layer. Apply transformations to create Silver data. Aggregate and refine the data to store it in the Gold layer.
- Data Serving: Connect Power BI to the Gold layer in Delta Lake. Create a Power BI report to visualize the weather data.
- Testing: Validate the data processing pipeline by generating test data. Ensure the data flows correctly from Azure Event Hubs through to Power BI.
- Deployment: Deploy the solution in a production environment. Monitor the data pipeline and adjust as needed for performance and scalability.
Notes on Real-Time Data Processing with Azure Databricks and Event Hubs
Output Modes in Spark Structured Streaming
| Output Mode | Behaviour |
|---|---|
| Complete | The entire updated result table is written to external storage. |
| Append | Only new rows appended in the result table since the last trigger are written to external storage. |
| Update | Only the rows that were updated in the result table since the last trigger are written to external storage. If the query doesn't contain aggregations, it is equivalent to Append mode. |
Checkpointing in Spark Structured Streaming
Checkpointing is used to prevent duplicate outputs during writeStream operations, even after job restarts or failures.
Windowing in Spark Structured Streaming
Windowing Behavior: The latest window will close when an event with an event time later than 3:25 is received. This is because the upper bound of the window is 3:20. So, an event time after 3:25 is greater than the upper bound plus 5 minutes.
Power BI Integration
To connect with Power BI, you can use Partner Connect for seamless integration between Databricks and Power BI.
 View the full project on GitHub
View the full project on GitHub